Though with a trade-off in space complexity, this strategy reduces the time complexity of the prior one. For every row, column, and submatrix we track the values we have already seen or visited using an unordered set.
We look for if the current cell value already exists in the matching row, column, or sub-grid as we iterate over the matrix and for each cell. Should a duplicate surface, the Sudoku board is void. The board arrangement is good if, after looking over all the cells, no duplicates are discovered.
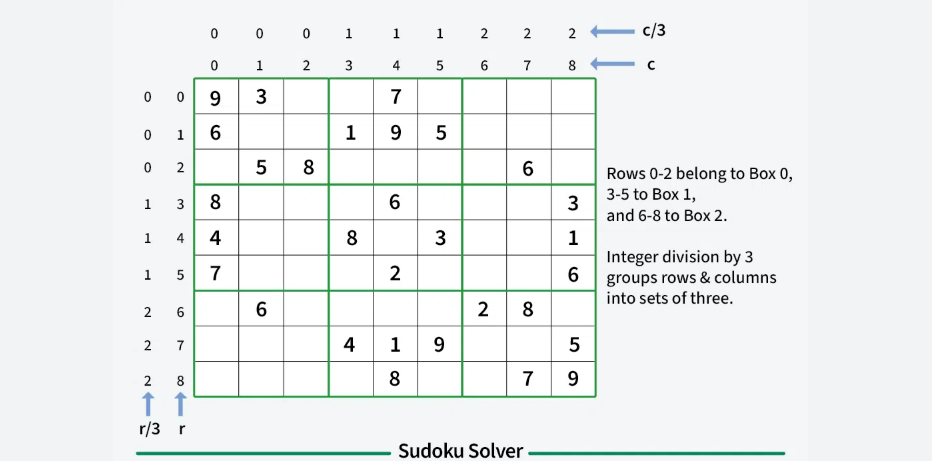
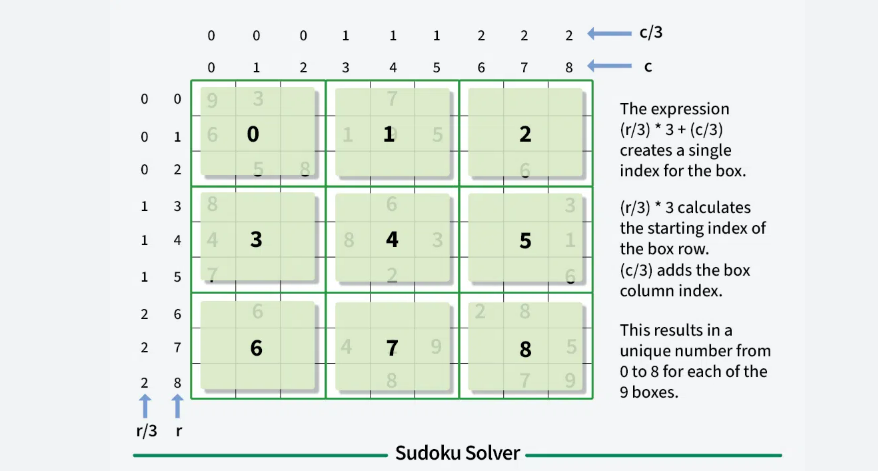
Important Observation: The sudoku matrix consists of nine 3x 3 submatrices; so, the formula (i / 3) * 3 + j / 3 will help one to determine the index of a given submatrix.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to check if the Sudoku matrix is valid
int isValid(vector<vector<int>> & mat) {
// Arrays of unordered sets to keep track of seen
// numbers in rows, columns, and subMatrix
unordered_set<int> rows[9];
unordered_set<int> cols[9];
unordered_set<int> subMat[9];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
// Get the value at the current cell
int val = mat[i][j];
// For empty (0), skip to the next cell
if (val == 0) continue;
// Check if the value already exists
// in the current row
if (rows[i].find(val) != rows[i].end()) {
// Duplicate found, return false
return false;
}
// Insert the value into the current row's set
rows[i].insert(val);
// Check if the value already exists
// in the current column
if (cols[j].find(val) != cols[j].end()) {
// Duplicate found, return false
return false;
}
// Insert the value into the current column's set
cols[j].insert(val);
// Calculate the index for the 3x3 box
int idx = (i / 3) * 3 + j / 3;
// Check if the value already exists
// in the current 3x3 box
if (subMat[idx].find(val) != subMat[idx].end()) {
// Duplicate found, return false
return false;
}
// Insert the value into the current box's set
subMat[idx].insert(val);
}
}
// If no duplicates were found, return true
return true;
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> mat = {
{9, 3, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{6, 0, 0, 1, 9, 5, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 5, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0},
{8, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3},
{4, 0, 0, 8, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1},
{7, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6},
{0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 8, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 4, 1, 9, 0, 0, 5},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 7, 9}
};
cout << (isValid(mat) ? "true" : "false") << "\n";
return 0;
}JAVA
import java.util.HashSet;
class GfG {
// Function to check if the Sudoku matrix is valid
static boolean isValid(int[][] mat) {
// Arrays of sets to track seen numbers in rows,
// columns, and subMatrices
HashSet<Integer>[] rows = new HashSet[9];
HashSet<Integer>[] cols = new HashSet[9];
HashSet<Integer>[] subMat = new HashSet[9];
// Initialize the sets
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
rows[i] = new HashSet<>();
cols[i] = new HashSet<>();
subMat[i] = new HashSet<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
int val = mat[i][j];
// Skip empty cells
if (val == 0) continue;
// Check for duplicates in the row
if (rows[i].contains(val)) return false;
rows[i].add(val);
// Check for duplicates in the column
if (cols[j].contains(val)) return false;
cols[j].add(val);
// Calculate the sub-matrix index
int idx = (i / 3) * 3 + (j / 3);
// Check for duplicates in the sub-matrix
if (subMat[idx].contains(val)) return false;
subMat[idx].add(val);
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] mat = {
{9, 3, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{6, 0, 0, 1, 9, 5, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 5, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0},
{8, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3},
{4, 0, 0, 8, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1},
{7, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6},
{0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 8, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 4, 1, 9, 0, 0, 5},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 7, 9}
};
System.out.println(isValid(mat) ? "true" : "false");
}
}Python
# Function to check if the Sudoku matrix is valid
def isValid(mat):
# Arrays of sets to track seen numbers in rows, cols
rows = [set() for _ in range(9)]
cols = [set() for _ in range(9)]
subMat = [set() for _ in range(9)]
# Loop through the Sudoku grid
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
val = mat[i][j]
# Skip empty cells
if val == 0:
continue
# Check for duplicates in the row
if val in rows[i]:
return False
rows[i].add(val)
# Check for duplicates in the column
if val in cols[j]:
return False
cols[j].add(val)
# Calculate the sub-matrix index
idx = (i // 3) * 3 + (j // 3)
# Check for duplicates in the sub-matrix
if val in subMat[idx]:
return False
subMat[idx].add(val)
return True
# Example sudoku board
mat = [
[9, 3, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[6, 0, 0, 1, 9, 5, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 5, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0],
[8, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3],
[4, 0, 0, 8, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1],
[7, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6],
[0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 8, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 4, 1, 9, 0, 0, 5],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 7, 9]
]
# Check if the Sudoku matrix is valid
print("true" if isValid(mat) else "false")C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
// Function to check if the Sudoku matrix is valid
static bool IsValid(int[, ] mat)
{
// Arrays of sets to track seen numbers in rows,
// cols
HashSet<int>[] rows = new HashSet<int>[ 9 ];
HashSet<int>[] cols = new HashSet<int>[ 9 ];
HashSet<int>[] subMat = new HashSet<int>[ 9 ];
// Initialize the sets
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
rows[i] = new HashSet<int>();
cols[i] = new HashSet<int>();
subMat[i] = new HashSet<int>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
int val = mat[i, j];
// Skip empty cells
if (val == 0)
continue;
// Check for duplicates in the row
if (rows[i].Contains(val))
return false;
rows[i].Add(val);
// Check for duplicates in the column
if (cols[j].Contains(val))
return false;
cols[j].Add(val);
// Calculate the sub-matrix index
int idx = (i / 3) * 3 + j / 3;
// Check for duplicates in the sub-matrix
if (subMat[idx].Contains(val))
return false;
subMat[idx].Add(val);
}
}
return true;
}
static void Main()
{
int[, ] mat = { { 9, 3, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 6, 0, 0, 1, 9, 5, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 5, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 8, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3 },
{ 4, 0, 0, 8, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 7, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6 },
{ 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 8, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 4, 1, 9, 0, 0, 5 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 7, 9 } };
Console.WriteLine(IsValid(mat) ? "true" : "false");
}
}JavaScript
// Function to check if the Sudoku matrix is valid
function isValid(mat){
// Arrays to track seen numbers in rows, cols, and
// subMatrices
let rows = Array.from({length : 9}, () => new Set());
let cols = Array.from({length : 9}, () => new Set());
let subMat = Array.from({length : 9}, () => new Set());
// Loop through the Sudoku grid
for (let i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
let val = mat[i][j];
// Skip empty cells
if (val === 0)
continue;
// Check for duplicates in the row
if (rows[i].has(val))
return false;
rows[i].add(val);
// Check for duplicates in the column
if (cols[j].has(val))
return false;
cols[j].add(val);
// Calculate the sub-matrix index
let idx
= Math.floor(i / 3) * 3 + Math.floor(j / 3);
// Check for duplicates in the sub-matrix
if (subMat[idx].has(val))
return false;
subMat[idx].add(val);
}
}
return true;
}
let mat = [
[ 9, 3, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 6, 0, 0, 1, 9, 5, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 5, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0 ],
[ 8, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3 ],
[ 4, 0, 0, 8, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 7, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6 ],
[ 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 8, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 4, 1, 9, 0, 0, 5 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 7, 9 ]
];
console.log(isValid(mat) ? "true" : "false");Time Complexity: O(n2), where each operation (findnig and inserting) on unordered set requires O(1) on average, iterating over all n x n cells causes O.
Auxiliary Space: O(n2) auxiliary space resulting from three arrays of n unordered sets one for rows, one for columns, and one for submatrices. Every set can save up to n elements, which results in O(n²) overall space use.
