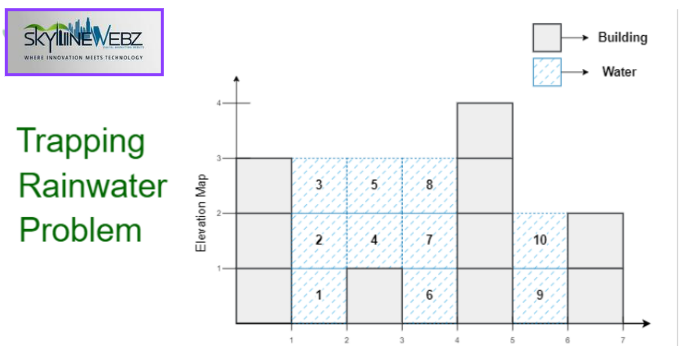
Optimal Method: Two Pointers O(n) Time and O(1) Space:
The strategy is mostly predicated on the following facts:
- Knowing the left max (max element in arr[0…left-1]) and right max (max element in arr[right+1…n-1], allows us to determine the amount of water either for arr[left] or arr[right].
- Should left max be less than the right max, we can choose arr[left]. Alternatively, we can choose arr[right].
- Should we choose arr[left], the remaining water would be left most minimally.
How can this be accomplished?
Let us examine the situation whereby left max is less than right max. We already have a bigger value in arr[right…n-1 so we know left max for arr[left] and the right max for it would not be less than left max.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int maxWater(vector<int> &arr) {
int left = 1;
int right = arr.size() - 2;
// lMax : Maximum in subarray arr[0..left-1]
// rMax : Maximum in subarray arr[right+1..n-1]
int lMax = arr[left - 1];
int rMax = arr[right + 1];
int res = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// If rMax is smaller, then we can decide the amount of water for arr[right]
if (rMax <= lMax) {
// Add the water for arr[right]
res += max(0, rMax - arr[right]);
// Update right max
rMax = max(rMax, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer as we have decided the amount of water for this
right -= 1;
} else {
// Add the water for arr[left]
res += max(0, lMax - arr[left]);
// Update left max
lMax = max(lMax, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer as we have decided water for this
left += 1;
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 0, 4};
cout << maxWater(arr) << endl;
return 0;
}C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to find the maximum amount of water that can be trapped
int maxWater(int arr[], int n) {
int left = 1;
int right = n - 2;
// lMax : Maximum in subarray arr[0..left-1]
// rMax : Maximum in subarray arr[right+1..n-1]
int lMax = arr[left - 1];
int rMax = arr[right + 1];
int res = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// If rMax is smaller, then we can decide the amount of water for arr[right]
if (rMax <= lMax) {
// Add the water for arr[right]
res += (rMax - arr[right]) > 0 ? (rMax - arr[right]) : 0;
// Update right max
rMax = rMax > arr[right] ? rMax : arr[right];
// Update right pointer as we have decided the amount of water for this
right -= 1;
} else {
// Add the water for arr[left]
res += (lMax - arr[left]) > 0 ? (lMax - arr[left]) : 0;
// Update left max
lMax = lMax > arr[left] ? lMax : arr[left];
// Update left pointer as we have decided water for this
left += 1;
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int arr[] = {2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 0, 4};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("%d\n", maxWater(arr, n));
return 0;
}Java
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// Function to find the maximum amount of water that can be trapped
static int maxWater(int[] arr) {
int left = 1;
int right = arr.length - 2;
// lMax : Maximum in subarray arr[0..left-1]
// rMax : Maximum in subarray arr[right+1..n-1]
int lMax = arr[left - 1];
int rMax = arr[right + 1];
int res = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// If rMax is smaller, then we can decide the amount of water for arr[right]
if (rMax <= lMax) {
// Add the water for arr[right]
res += Math.max(0, rMax - arr[right]);
// Update right max
rMax = Math.max(rMax, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer as we have decided the amount of water for this
right -= 1;
} else {
// Add the water for arr[left]
res += Math.max(0, lMax - arr[left]);
// Update left max
lMax = Math.max(lMax, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer as we have decided water for this
left += 1;
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 0, 4};
System.out.println(maxWater(arr));
}
}Python
# Function to find the maximum amount of water that can be trapped
def maxWater(arr):
left = 1
right = len(arr) - 2
# lMax : Maximum in subarray arr[0..left-1]
# rMax : Maximum in subarray arr[right+1..n-1]
lMax = arr[left - 1]
rMax = arr[right + 1]
res = 0
while left <= right:
# If rMax is smaller, then we can decide the amount of water for arr[right]
if rMax <= lMax:
# Add the water for arr[right]
res += max(0, rMax - arr[right])
# Update right max
rMax = max(rMax, arr[right])
# Update right pointer as we have decided the amount of water for this
right -= 1
else:
# Add the water for arr[left]
res += max(0, lMax - arr[left])
# Update left max
lMax = max(lMax, arr[left])
# Update left pointer as we have decided water for this
left += 1
return res
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 0, 4]
print(maxWater(arr))C#
using System;
class GfG {
// Function to find the maximum amount of water that can be trapped
static int maxWater(int[] arr) {
int left = 1;
int right = arr.Length - 2;
// lMax : Maximum in subarray arr[0..left-1]
// rMax : Maximum in subarray arr[right+1..n-1]
int lMax = arr[left - 1];
int rMax = arr[right + 1];
int res = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// If rMax is smaller, then we can decide the amount of water for arr[right]
if (rMax <= lMax) {
// Add the water for arr[right]
res += Math.Max(0, rMax - arr[right]);
// Update right max
rMax = Math.Max(rMax, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer as we have decided the amount of water for this
right -= 1;
} else {
// Add the water for arr[left]
res += Math.Max(0, lMax - arr[left]);
// Update left max
lMax = Math.Max(lMax, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer as we have decided water for this
left += 1;
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
int[] arr = {2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 0, 4};
Console.WriteLine(maxWater(arr));
}
}JavaScript
// Function to find the maximum amount of water that can be trapped
function maxWater(arr) {
let left = 1;
let right = arr.length - 2;
// lMax : Maximum in subarray arr[0..left-1]
// rMax : Maximum in subarray arr[right+1..n-1]
let lMax = arr[left - 1];
let rMax = arr[right + 1];
let res = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// If rMax is smaller, then we can decide the amount of water for arr[right]
if (rMax <= lMax) {
// Add the water for arr[right]
res += Math.max(0, rMax - arr[right]);
// Update right max
rMax = Math.max(rMax, arr[right]);
// Update right pointer as we have decided the amount of water for this
right -= 1;
} else {
// Add the water for arr[left]
res += Math.max(0, lMax - arr[left]);
// Update left max
lMax = Math.max(lMax, arr[left]);
// Update left pointer as we have decided water for this
left += 1;
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [2, 1, 5, 3, 1, 0, 4];
console.log(maxWater(arr));